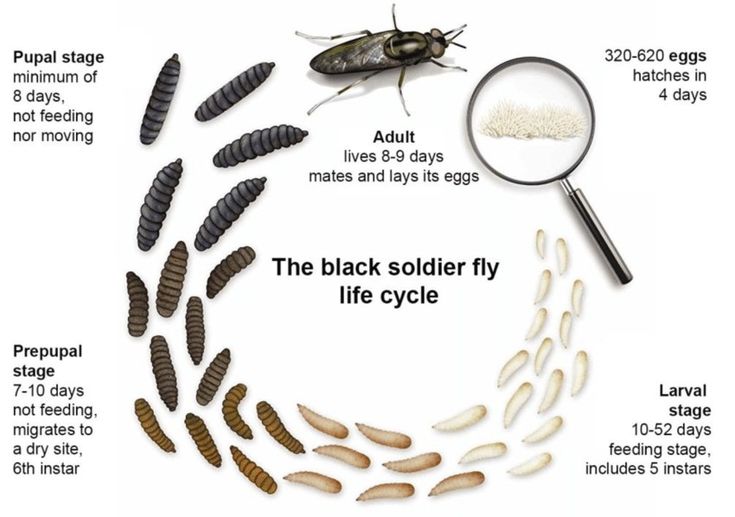
Understanding the life cycle of Black Soldier Flies (BSFs) is crucial for successful farming. Each stage of their development plays a unique role in waste management and protein production, making BSFs a sustainable and efficient farming option. Below is an overview of the BSF life cycle and its significance for farmers.
Egg Stage
The life cycle begins with eggs laid by adult female flies. Females typically deposit eggs near decaying organic matter, ensuring food for the hatching larvae. Eggs hatch within 3–4 days under optimal conditions, initiating the next stage of the life cycle.

Larval Stage
The larval stage is the most important for BSF farming. During this period, larvae consume large amounts of organic waste, converting it into valuable protein and biofertilizer. This stage lasts about 14–18 days, depending on temperature and feeding conditions. Farmers often harvest the mature larvae at this stage for use as animal feed or other applications.

On a similar note, at Kimd Group of Companies, we support beginner farmers by offering tailored business proposal writing services and design plans for various animal capacities. Therefore whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand, we provide the resources and expertise to help you succeed in the farming industry.
Pupal Stage
After the larval stage, BSFs enter the pupal stage, during which they transform into adult flies. Pupae are typically darker in color and do not require food, as they rely on stored energy. This stage lasts approximately 5–10 days and is critical for the fly’s metamorphosis.

Adult Stage
Adult BSFs emerge from the pupae to complete the cycle. These flies live for 5–8 days and focus solely on reproduction, as they do not eat in this stage. They rely on energy reserves accumulated during the larval stage. Farmers must create a conducive environment for mating to ensure a continuous cycle.

Conclusion
The life cycle of Black Soldier Flies demonstrates their efficiency and versatility in waste management and protein production. By understanding each stage, farmers can optimize conditions to maximize productivity and maintain a sustainable farming system.
