Raising doves for meat production is a growing niche in poultry farming due to the increasing demand for their tender and flavorful meat. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced farmer, success in dove meat production requires proper planning, feeding, and management practices. Here’s a comprehensive guide to raising doves for meat.
1. Choose the Right Breed
Selecting the right breed is crucial for meat production. Some of the best dove breeds for meat include:
- King Doves: Known for their large size and fast growth, ideal for commercial meat production.
- Utility Doves: A group of doves bred specifically for meat due to their high yield and efficient feed conversion.
- Homing Doves: Although smaller, they can also be raised for meat on a small scale.

On a similar note, at Kimd Group of Companies, we support beginner farmers by offering tailored business proposal writing services and design plans for various animal capacities. Therefore whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand, we provide the resources and expertise to help you succeed in the farming industry.
2. Set Up Housing for Meat Doves
Doves raised for meat require spacious, clean, and predator-proof housing. Follow these housing guidelines:
- Space: Provide at least 2 square feet per dove to ensure comfort and reduce stress.
- Ventilation: Maintain good airflow to prevent respiratory issues.
- Nesting Areas: Include nesting boxes for breeding pairs to encourage reproduction.
- Cleanliness: Regularly clean the housing to prevent diseases and maintain hygiene.
3. Provide a Nutritious Diet
A balanced diet is critical for fast growth and high-quality meat. The diet should include:
- Grains and Seeds: Millet, sorghum, and wheat as the primary food sources.
- Protein Supplements: Include peas, lentils, or commercial protein-rich feeds.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Add supplements to ensure optimal growth and health.
Provide clean, fresh water at all times and monitor their feeding to avoid underfeeding or wastage.

4. Breeding for Meat Production
To maintain a consistent supply of meat doves, establish a breeding program:
- Select healthy, mature breeding pairs.
- Ensure the breeding environment is stress-free and well-maintained.
- Replace older breeders with younger, more productive birds regularly.
Breeding pairs will produce 1–2 eggs per clutch, and chicks, known as squabs, are ready for meat harvesting at 3–4 weeks of age.

5. Monitor Health and Hygiene
Healthy doves produce better quality meat. Implement these practices to maintain flock health:
- Vaccinate: Protect your flock from common diseases like Newcastle disease.
- Regular Health Checks: Monitor for signs of illness, such as lethargy or loss of appetite.
- Parasite Control: Regularly check for external and internal parasites and treat promptly.
Ensure housing, feeding areas, and water sources are kept clean to reduce the risk of infections.

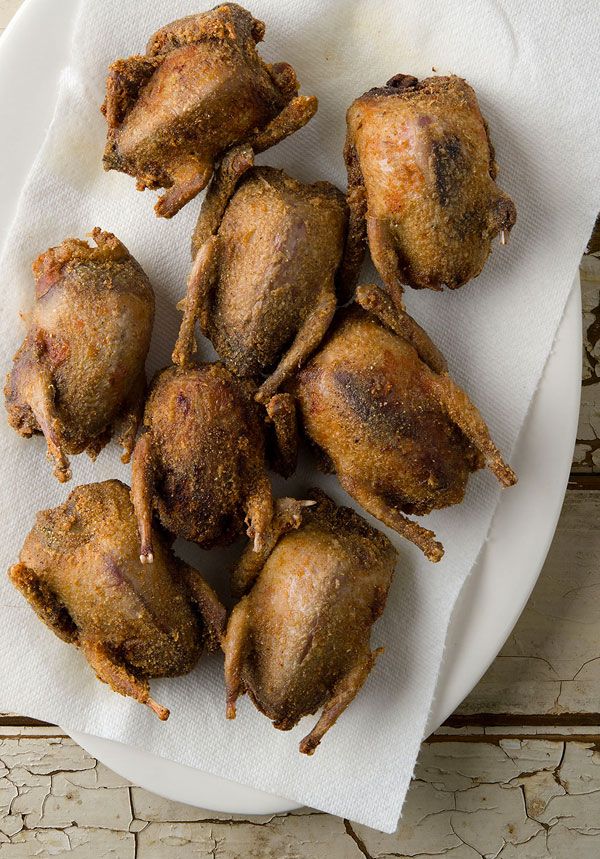
6. Harvesting and Processing Squabs
Squabs are typically harvested between 21 and 30 days old when their meat is most tender. At this stage, they haven’t yet developed flight feathers, which simplifies processing.
- Handle squabs humanely during harvesting.
- Process under hygienic conditions to meet food safety standards.

7. Market Your Dove Meat
Dove meat is often marketed as a delicacy. Target niche markets, such as restaurants, gourmet food suppliers, and local farmers’ markets. Highlight the unique qualities of dove meat, including its tenderness and rich flavor, to attract customers.

Conclusion
Raising doves for meat production can be a profitable venture when done correctly. By selecting the right breed, providing proper care, and maintaining a consistent breeding program, you can produce high-quality dove meat to meet market demand. With careful planning and attention to detail, dove meat farming can become a sustainable and rewarding business.
