Breeding practices play a pivotal role in beef cattle production, influencing herd fertility, genetic improvement, and overall productivity. Implementing effective breeding strategies ensures a steady supply of high-quality calves, improves meat quality, and enhances profitability. Here are key practices for successful cattle breeding.
1. Selection of Superior Breeding Stock
Choosing high-performing bulls and cows with desirable traits is fundamental. Traits such as fertility, growth rate, carcass quality, and disease resistance should guide selection. Using tools like Expected Progeny Differences (EPDs) helps evaluate the genetic potential of breeding animals for specific traits.
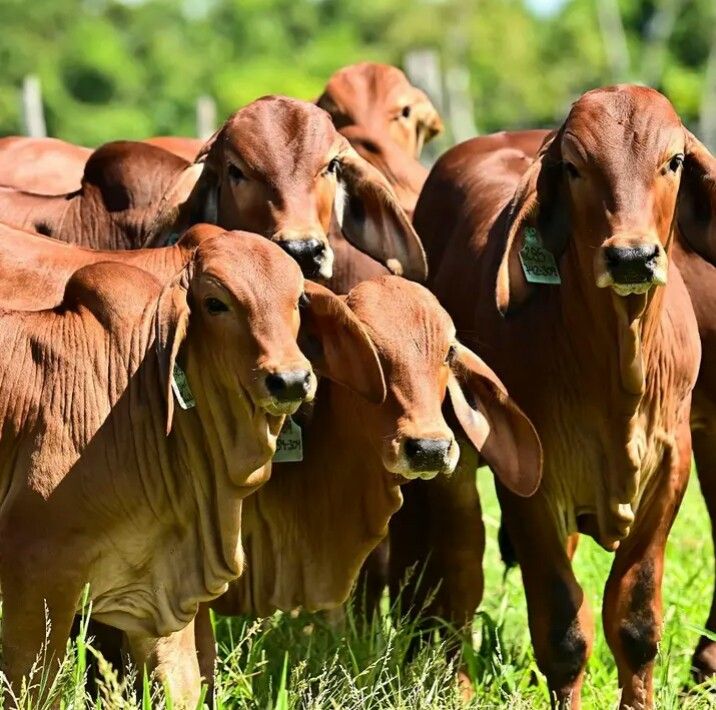

2. Employing Crossbreeding Programs
Crossbreeding combines the best traits of different breeds and boosts productivity through hybrid vigor (heterosis). For example, crossing Brahman cattle, known for heat tolerance, with British breeds like Angus, valued for meat quality, produces offspring with superior traits. Crossbreeding programs should be carefully planned to align with production goals.
3. Managing Breeding Seasons
Establishing defined breeding seasons ensures calves are born during optimal times, such as when forage availability is high. Concentrated calving periods make herd management more efficient, simplifying vaccination, weaning, and marketing processes.
On a similar note, at Kimd Group of Companies, we support beginner farmers by offering tailored business proposal writing services and design plans for various animal capacities. Therefore whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand, we provide the resources and expertise to help you succeed in the farming industry.
4. Artificial Insemination (AI)
AI allows farmers to access superior genetics from top-performing bulls worldwide without owning them. This practice ensures genetic diversity and accelerates herd improvement. Proper timing of insemination, based on estrus detection, is critical for success.
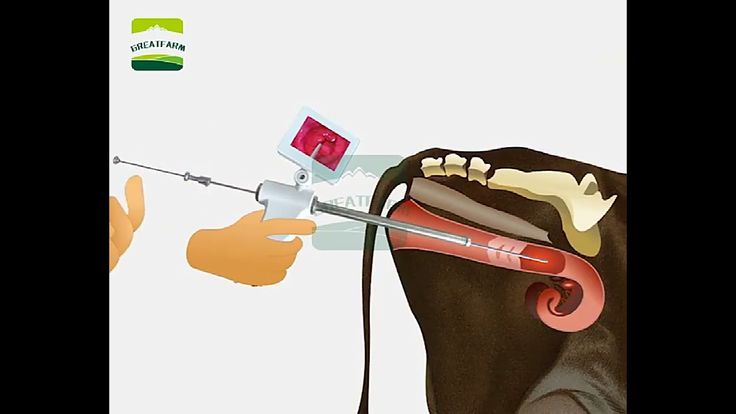
5. Monitoring Reproductive Health
Regular health checks and reproductive evaluations of both bulls and cows are essential. Issues like infertility, infections, or nutritional deficiencies should be promptly addressed. Pregnancy checks help identify open cows, enabling timely re-breeding or culling decisions.
6. Nutrition for Breeding Cattle
Nutritional management significantly affects fertility. Breeding animals should receive diets rich in energy, protein, and minerals to maintain body condition. Overfeeding or underfeeding can negatively impact reproductive performance, so diets should be balanced based on body condition scores (BCS).

7. Record-Keeping and Performance Tracking
Maintaining detailed records of breeding dates, calving intervals, and genetic performance helps monitor and improve herd productivity. Records guide future breeding decisions and identify underperforming animals for culling.
Conclusion
Effective breeding practices are vital for sustainable beef cattle production. By focusing on superior genetic selection, structured breeding programs, and proper nutrition, farmers can improve herd productivity and profitability. Modern tools like artificial insemination and performance tracking further enhance breeding efficiency, making it a cornerstone of successful cattle farming.
