Artificial insemination (AI) is an advanced breeding technique used in goat farming to improve genetics, enhance productivity, and control reproduction efficiently. This method allows farmers to use superior male genetics without needing to keep multiple bucks, reducing costs and risks associated with natural mating.
Benefits of Artificial Insemination
One of the main advantages of AI is genetic improvement. Farmers can access high-quality semen from proven bucks worldwide, leading to better milk production, faster growth rates, and improved disease resistance in offspring. AI also reduces the risk of disease transmission, which is common in natural mating. Additionally, it allows for better control over the breeding season, ensuring synchronized kidding and more efficient farm management.

Besides goat farming, at Kimd Group of Companies, we support beginner farmers by offering tailored business proposal writing services and design plans for various animal capacities. Therefore whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand, we provide the resources and expertise to help you succeed in the farming industry.
Preparing for Artificial Insemination
Successful AI in goats requires careful preparation. The does should be in good health, with proper nutrition and regular deworming to ensure high conception rates. Farmers must accurately detect the heat cycle, as AI is most effective when performed during peak estrus. Signs of heat include restlessness, increased vocalization, tail wagging, and swelling of the vulva. If natural heat detection is difficult, hormonal synchronization using prostaglandins or progesterone treatments can help regulate the reproductive cycle.
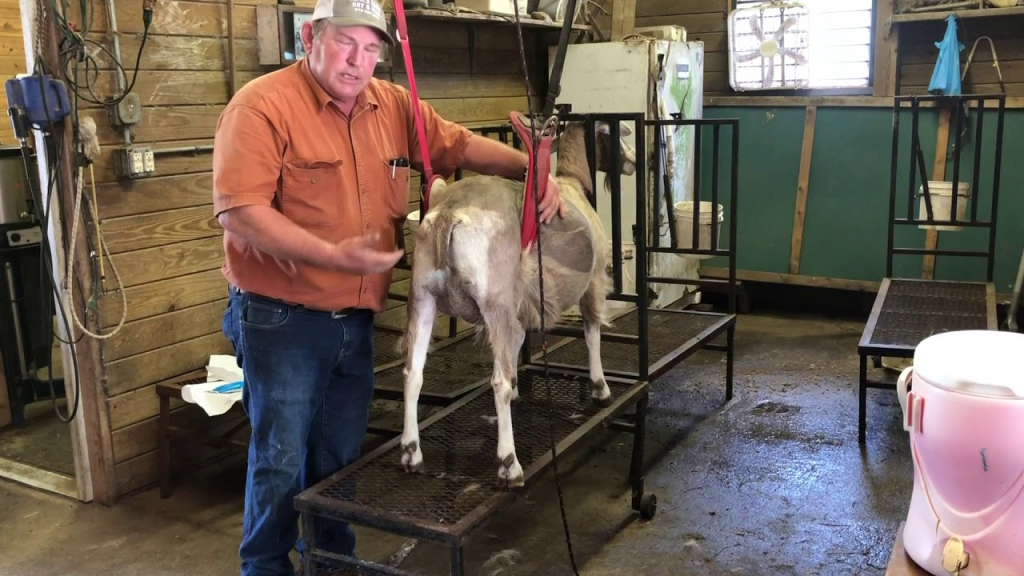

The Artificial Insemination Process
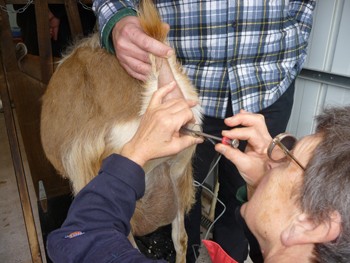
The AI process involves collecting and storing semen from high-quality bucks under controlled conditions. The semen can be fresh, chilled, or frozen, with frozen semen requiring liquid nitrogen storage. During insemination, the semen is deposited into the reproductive tract of the doe using specialized equipment. The timing is crucial, as insemination should ideally occur 12 to 18 hours after heat detection for the best conception rates. Proper handling and hygiene during the procedure increase the chances of success.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, AI requires technical knowledge and skill to be effective. Farmers may need professional assistance or training to perform AI correctly. Additionally, factors such as poor heat detection, improper semen handling, and low-quality nutrition can reduce success rates. In some cases, natural mating may still be necessary if AI fails or if suitable resources are unavailable.
Conclusion
Artificial insemination is a valuable tool in goat farming, offering genetic improvement, disease prevention, and better breeding control. With proper preparation, heat detection, and semen handling, farmers can achieve higher productivity and efficiency in their herds.
