Rabbit farming is an increasingly popular venture due to its low startup costs, high reproduction rate, and profitability. Whether for meat, fur, or as pets, rabbits offer a sustainable farming option with minimal space requirements. This guide provides essential information for beginners looking to start a successful rabbit farming business.
Choosing the Right Rabbit Breeds
Selecting the right breed is crucial for a successful rabbit farm. Common meat breeds include New Zealand White, Californian, and Flemish Giant, known for their fast growth and high meat yield. For fur production, Angora rabbits are ideal due to their thick, soft wool. Pet breeds such as Holland Lop and Netherland Dwarf are popular due to their small size and friendly nature.

Speaking of Rabbit Farming, at Kimd Group of Companies, we support beginner farmers by offering tailored business proposal writing services and design plans for various animal capacities. Therefore whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand, we provide the resources and expertise to help you succeed in the farming industry
Setting Up Rabbit Housing
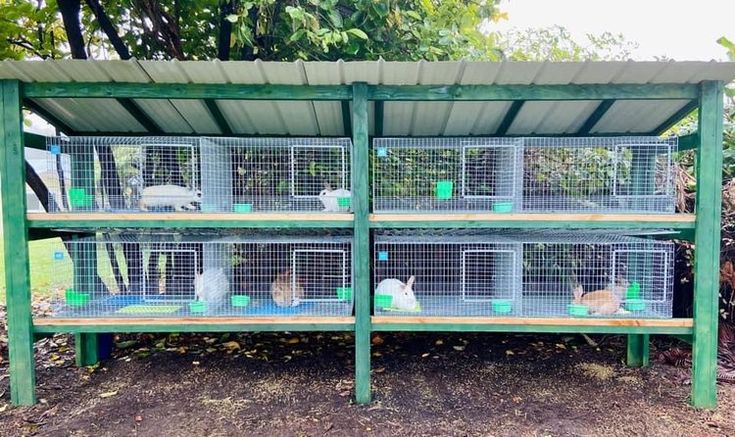
Proper housing ensures healthy growth and productivity. Rabbits require clean, well-ventilated hutches or cages to prevent disease and stress. The housing should be elevated to allow waste disposal, and each cage should provide ample space for movement. Wire mesh flooring helps maintain hygiene, while shaded areas protect rabbits from extreme temperatures.

Feeding and Nutrition
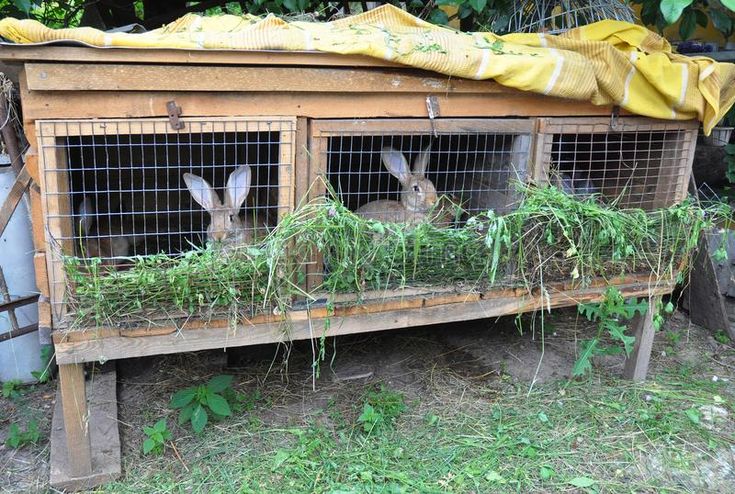
A balanced diet is vital for healthy rabbits. Their diet consists mainly of hay, fresh vegetables, and commercial rabbit pellets rich in fiber, proteins, and minerals. Fresh water should be available at all times to keep them hydrated. Overfeeding grains or sugary treats can lead to digestive issues, so a well-regulated feeding schedule is essential.

Breeding and Reproduction
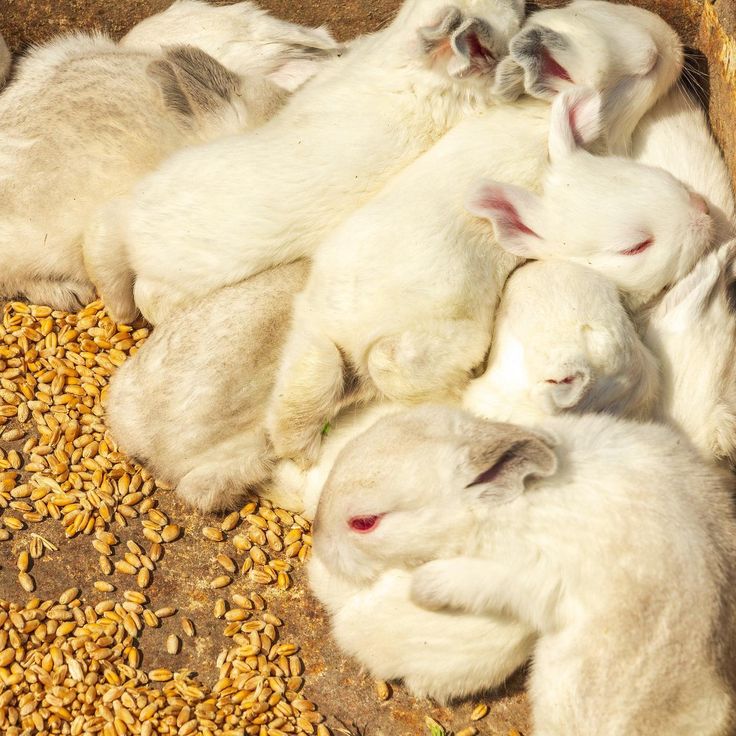
Rabbits have a high reproductive rate, making them ideal for commercial farming. A healthy doe can produce up to eight litters annually, with each litter containing 6–12 kits. Mating should be carefully managed to avoid overbreeding, and pregnant does should have separate nesting areas for safe delivery. Kits should stay with their mothers for at least four weeks before weaning.

Disease Management and Biosecurity
Maintaining strict hygiene reduces the risk of disease outbreaks. Common rabbit diseases include pasteurellosis, coccidiosis, and ear mites. Regular health checks, vaccinations, and proper waste management help prevent infections. Quarantining new or sick rabbits prevents disease transmission, ensuring a healthy population.
Marketing and Profitability
Rabbit products have a growing market demand. Rabbit meat is lean, nutritious, and widely consumed, while rabbit fur is valuable in textile industries. Additionally, selling breeding stock to new farmers can be lucrative. Effective marketing strategies, including social media promotions, local advertisements, and partnerships with restaurants, increase sales and profitability.
Conclusion
Rabbit farming is an excellent agribusiness venture with high returns on investment. By selecting the right breeds, providing proper housing, feeding a balanced diet, and maintaining strict biosecurity, farmers can achieve success in rabbit production. With proper planning and management, rabbit farming can be a sustainable and profitable business.
